|
WE
CARE
MDS
offers quality and convenient patient care demonstrated by the hundreds of
satisfied patients and practitioners who have used our diagnostic services. MDS offers the convenience of allowing the
patient/practitioner to choose where and when the diagnostic tests are
performed with operating hours to meet off-hour and weekend
schedules.
| ABOUT
NCV TESTING (Contributed
with permission by MedlinePlus.com) |

click
image to enlarge
|
What
is an NCV test and why is it performed?
An
NCV test determines the speed of conduction of impulses through a nerve.
This test is used to diagnose nerve damage or destruction.
How
the test is performed
The
nerve is stimulated, usually with surface electrodes, which are patch-like
electrodes (similar to those used for ECG) placed on the skin over the nerve
at various locations. One electrode stimulates the nerve with a very mild
electrical impulse. The resulting
electrical activity is recorded by the other electrodes. The distance
between electrodes and the time it takes for electrical impulses to travel
between electrodes are used to calculate the nerve conduction velocity.
How to prepare for the test
Normal
body temperature must be maintained (low body temperature slows nerve
conduction).
How
the test feels
The
impulse given may feel like an electric shock. Depending on how strong the
stimulus is, the patient will feel it at varying degrees. It may be
uncomfortable for some patients (though only during the actual test and
there should be no residual pain once the test is completed). Often
the nerve conduction test is followed by an EMG (electromyography) which
involves needles being placed into the muscle and the patient being asked to
contract that muscle. This can be uncomfortable during the test, and
subsequent muscle soreness from the needles may be experienced as well.
Risks
There
are essentially no risks
Normal
& Abnormal results - what do they mean?
Click
here
for more information
| ABOUT EMG TESTING (Contributed
with permission by MedlinePlus.com) |
click
image to enlarge
|
What
is an EMG test and why is it performed?
A
test that measures muscle response to nervous stimulation (electrical
activity within muscle fibers). EMG is most often used when people
have symptoms of weakness, and examination shows impaired muscle strength.
It can help to differentiate primary muscle conditions from muscle weakness
caused by neurological disorders. EMG can be used to differentiate between
true weakness and reduced use because of pain or lack of motivation.
How
the test is performed
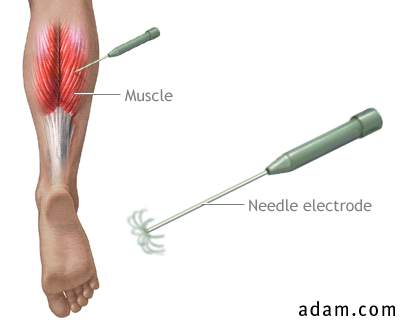
A
needle electrode is inserted through the skin into the muscle. The
electrical activity detected by this electrode is displayed on an
oscilloscope (and may be displayed audibly through a speaker). Because
skeletal muscles are isolated and often large units, each electrode gives
only an average picture of the activity of the selected muscle. Several
electrodes may need to be placed at various locations to obtain an accurate
study.
After placement of the electrode(s), you may be asked to contract the muscle
(for example, by bending the arm). The presence, size, and shape of the wave
form produced on the oscilloscope (the action potential) provide information
about the ability of the muscle to respond to nervous stimulation.
Each muscle
fiber that contracts will produce an action potential, and the size of the
muscle fiber affects the rate (how frequently an action potential occurs)
and size (amplitude) of the action potential(s).
How to prepare for the test
No
special preparation is usually necessary.
How
the test feels
There
may be some discomfort with insertion of the electrodes (similar to an
intramuscular injection). Afterward, the examined muscle may feel tender or
bruised for a few days.
Risks
Bleeding
and Infection at the electrode sites (minimal risk)
Normal
& Abnormal results - what do they mean?
Click
here
for more information
SCHEDULING
AN APPOINTMENT
Patients
usually are scheduled for NCV or EMG testing through their practitioner.
Please contact your referring practitioner to schedule an appointment with us.
PAYMENT
Most
insurance plans will cover NCV/EMG tests.
|


